Deep groove ball bearings are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including machinery, automotive systems, and industrial equipment. They are designed to support radial and axial loads while enabling smooth and efficient rotation. Here are some key design principles and features of deep groove ball bearings:
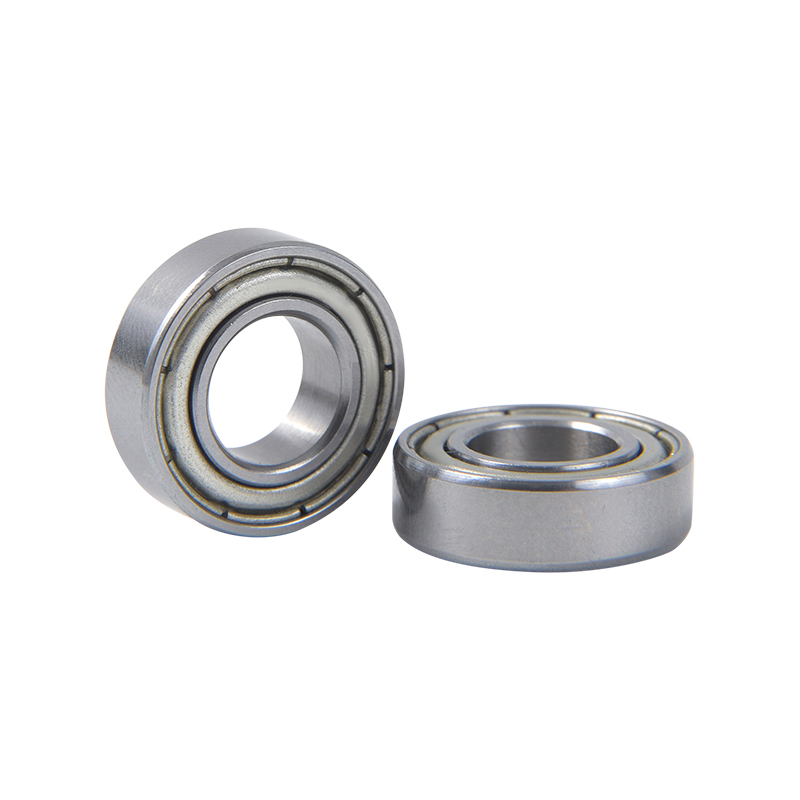
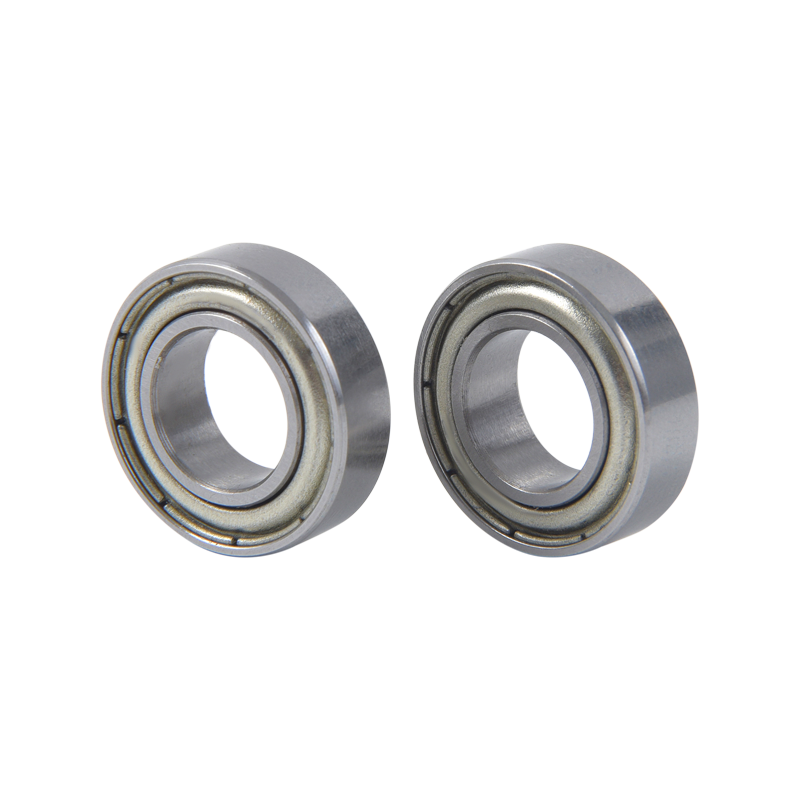
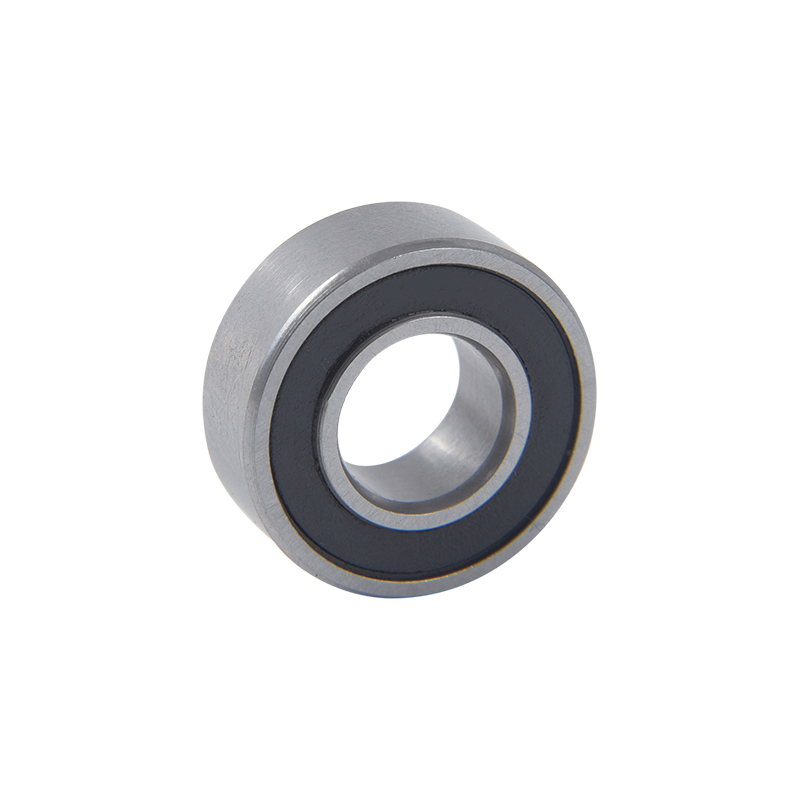
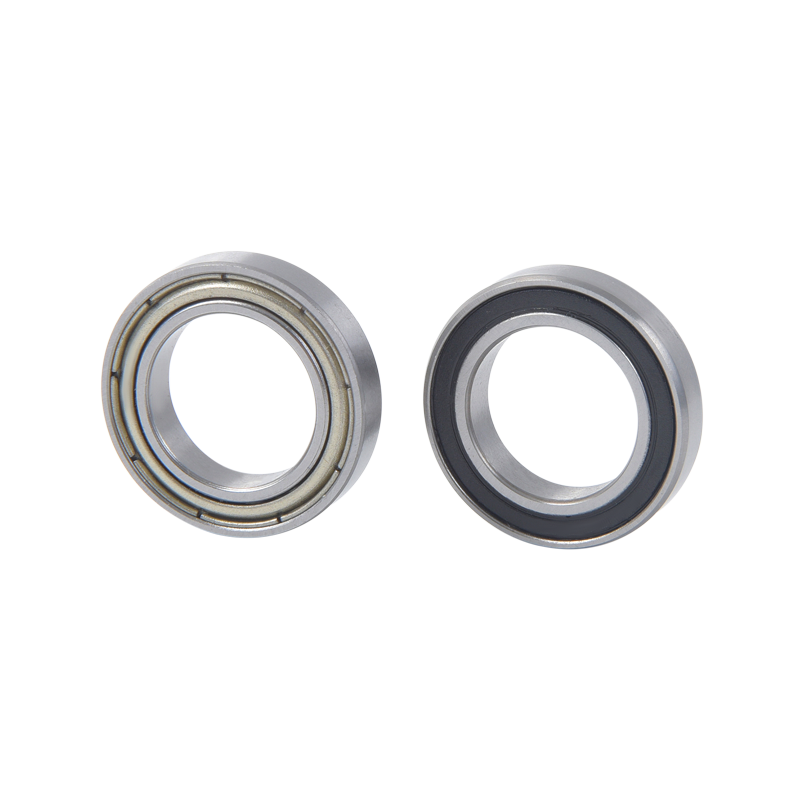
Geometry: Deep groove ball bearings consist of an inner ring, an outer ring, a cage, and a set of balls. The inner and outer rings have a circular track with a groove that forms the raceways for the balls. The geometry of these raceways is designed to optimize load distribution and minimize friction.
Load capacity: Deep groove ball bearings can handle both radial and axial loads. The number and size of the balls, as well as the curvature of the raceways, determine the load-carrying capacity of the bearing. The larger the balls and the greater their number, the higher the load capacity.
Cage design: The cage in a deep groove ball bearing keeps the balls separated and evenly spaced. It prevents contact between the balls, reducing friction and wear. The cage can be made of various materials, such as steel, brass, or synthetic polymers, depending on the application requirements.
Lubrication: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of deep groove ball bearings. Lubricants reduce friction and prevent metal-to-metal contact between the rolling elements and raceways. Common lubrication methods include grease packing, oil bath, or oil mist systems.
Sealing and shielding: Deep groove ball bearings can be equipped with seals or shields to protect against contamination, such as dust, dirt, or moisture. Seals provide better protection but can generate more heat due to increased friction. Shields offer less protection but result in lower friction.
Clearance: The internal clearance of a deep groove ball bearing refers to the space between the balls and raceways when the bearing is not under load. It affects the bearing's performance, including its operating temperature, noise level, and rotational speed. Different applications may require specific clearance values.
Material selection: The rings and balls of deep groove ball bearings are typically made of high-quality bearing steel, such as chrome steel or stainless steel. These materials offer excellent hardness, fatigue resistance, and dimensional stability. In special cases, ceramic balls may be used to enhance performance in high-speed or high-temperature applications.
Tolerance and precision: Deep groove ball bearings are manufactured with tight tolerances to ensure consistent performance. Precision bearings are designed for applications that demand high rotational accuracy and minimal vibration or noise.
Bearing play: Deep groove ball bearings can be designed with different levels of internal play, depending on the application requirements. Play refers to the axial movement of the inner and outer rings relative to each other. Some applications require minimal play, while others may benefit from slight axial movement to compensate for thermal expansion or misalignment.
Application-specific design: Deep groove ball bearings come in various sizes and designs to meet specific application needs. They can be optimized for high-speed operation, high-temperature environments, corrosive conditions, or other demanding requirements.
It's important to note that deep groove ball bearing design principles can vary across manufacturers and specific bearing models. Consulting the manufacturer's documentation and engineering specifications is recommended for detailed information on a particular bearing design.











 No. 7, Tangchuang Garden, Yangshan Village, Di Tang Street, Yuyao City, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province, China.
No. 7, Tangchuang Garden, Yangshan Village, Di Tang Street, Yuyao City, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province, China.
 +86-15706849036
+86-15706849036 +86-0574-63267578
+86-0574-63267578 +86-0574-63265856
+86-0574-63265856
